Big Data for What?
Big data analytics is the process of examining large data sets to uncover hidden patterns, unknown correlations, market trends, customer preferences and other useful business information. The analytical findings can lead to more effective marketing, new revenue opportunities, better customer service, improved operational efficiency, competitive advantages over rival organizations and other business benefits.
Big Data for Where?
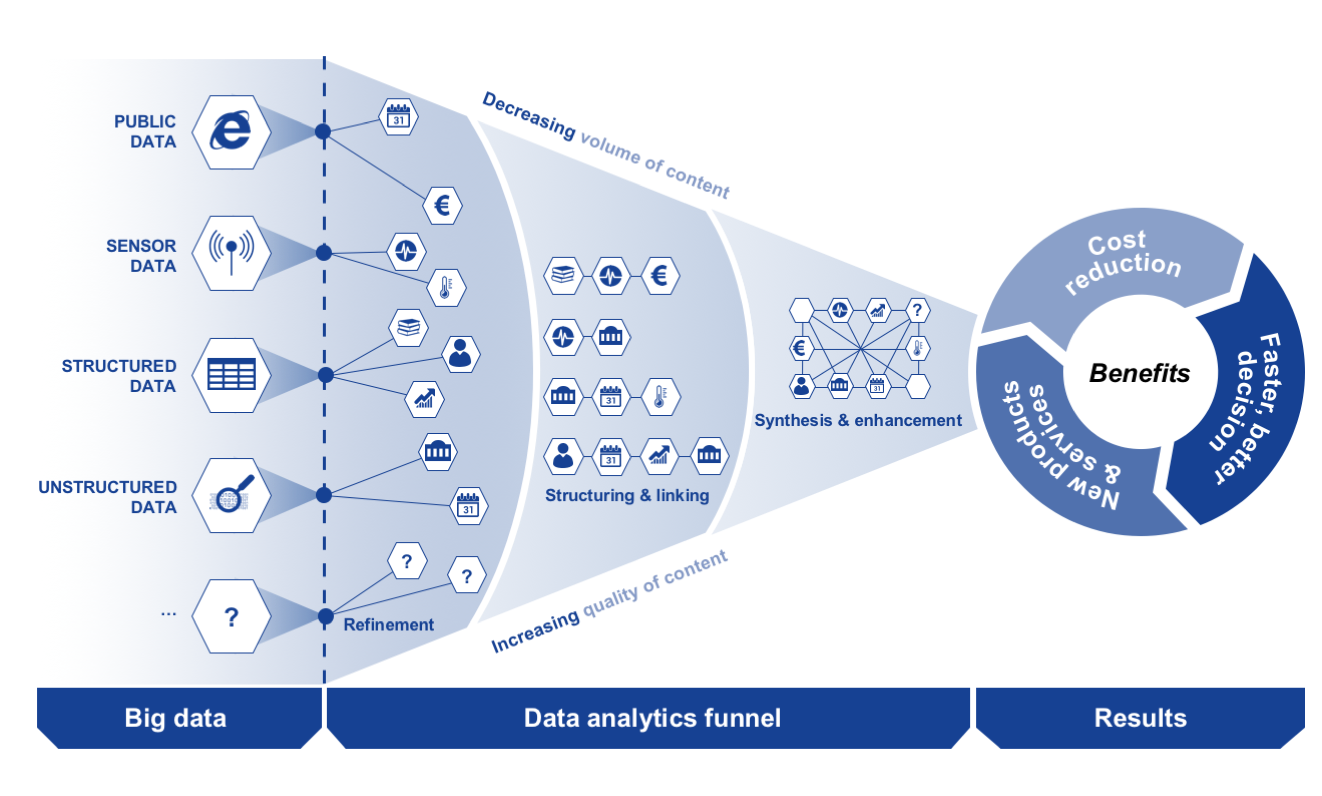
Big data analytics is the use of advanced analytic techniques against very large, diverse data sets that include different types such as structured/unstructured and streaming/batch, and different sizes from terabytes to zettabytes. Big data is a term applied to data sets whose size or type is beyond the ability of traditional relational databases to capture, manage, and process the data with low-latency. And it has one or more of the following characteristics – high volume, high velocity, or high variety. Big data comes from sensors, devices, video/audio, networks, log files, transactional applications, web, and social media – much of it generated in real time and in a very large scale.
Big Data for Who?
Analyzing big data allows analysts, researchers, and business users to make better and faster decisions using data that was previously inaccessible or unusable. Using advanced analytics techniques such as text analytics, machine learning, predictive analytics, data mining, statistics, and natural language processing, businesses can analyze previously untapped data sources independent or together with their existing enterprise data to gain new insights resulting in significantly better and faster decisions.
Advantages of using big data in business:
- Better decision making
- Innovation of new business strategies
- Improvement in existing workflow
- Product price optimization
- Forecasting and monitoring of business
- Diversify revenue streams to boost company